Now Enrolling for Adult, Adolescent, and Parent Programs!
What is DBT?
Intro to DBT: Development, Structure, and Focus
Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) is a comprehensive behavioral intervention designed to treat individuals with severe mental disorders and out-of-control cognitive, emotional and behavioral patterns.
It has been commonly viewed as a treatment for individuals meeting criteria for Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD) with chronic and high-risk suicidality, substance dependence or other disorders. However, over the years, data has emerged demonstrating that DBT is also effective for a wide range of other disorders and problems, most of which are associated with difficulties regulating emotions and associated cognitive and behavioral patterns.
It is also assumed that there are multiple causes as opposed to a single factor affecting the client.
In Dialectical Behavioral Therapy, “dialectical” means, A synthesis or integration of opposites (aka- finding the balance between opposites). In DBT, the main “dialectical” tension, or balance, is between the opposite ideas of ACCEPTANCE and CHANGE. In this framework, DBT therapists balance treatment strategies of validation and problem solving.
Founder of DBT
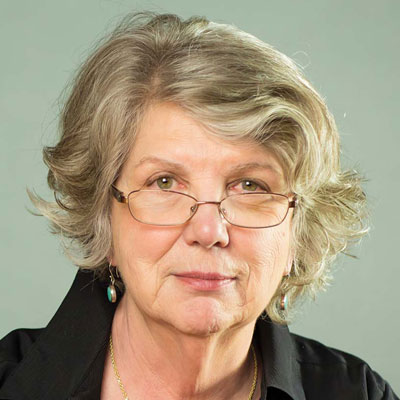

Marsha M. Linehan, American Psychologist, Founder of DBT
“My main goal for people who come into therapy is that they get out of hell…and that they stay out of hell…to build a life worth living.”
There are Four Stages of DBT, as Follows:
Pretreatment
Focuses on orienting the client to the structure and philosophy of DBT. The client begins to use the Diary Card, create values-based goals, and establishes therapy agreements between therapist and client. The Pretreatment phase ends when the client begins attending skills group.
Stage 1
Focuses on the client learning and using skills (skills acquisition) to target Emotional Dysregulation, Cognitive Instability, Interpersonal Instability, Behavior Instability and Self Instability. The client participates in 3 skills groups and repeats each group twice. This stage lasts for approximately 18 months – or until the client graduates from the comprehensive DBT program.
Stage 2
Stage 3
Stage 4
Focuses on attaining sense of joy and freedom. This stage is sometimes a type of “maintenance” phase, and the parameters are established between the therapist and client to help them continue experiencing joy and freedom in their lives.
Comprehensive Dialectical Behavioral Therapy (DBT)
Successful DBT therapy utilizes Skills Groups, Therapy, and Support to assist you in
building a life worth living.
Therapy
50 Minute Sessions
Weekly Individual
Therapy with your
own therapist
Skills Groups
2 Hour Sessions
Mindfulness
Distress Tolerance
Interpersonal Effectiveness
Emotional Regulation
Walk the Middle Path
(For adolescents)

Support
Brief Phone Call
24/7 Telephone Coaching

Consultation
Weekly Between Therapists
Your therapist
continually strengthens
and improves their
DBT expertise
through consultation
with other
DBT therapists
Therapists adhere to the following hierarchy of DBT Treatment Priorities, or Treatment Hierarchy, during individual therapy sessions, as follows:
1
Decrease Suicidal and/or Self-Injurious Behaviors
2
3
Address Quality-of-Life Behaviors
4
DBT Skills Groups
Skills Trainings Modules for Adults include Core Mindfulness (first 3 weeks of each group), Emotion Regulation (14 weeks), Interpersonal Effectiveness (10 weeks) and Distress Tolerance (10 weeks). For Parents, Families and Adolescents, skills training modules include Core Mindfulness (first 2 weeks of each group), Emotion Regulation (7 weeks), Interpersonal Effectiveness (6 weeks), Distress Tolerance (6 weeks), and Walk The Middle Path (6 weeks). The DBT Center of Utah also provides a 4-week orientation-to-DBT group when a client is beginning DBT treatment.
Skills group training is delivered in a group format that meets one time per week for 1.5 – 2 hours. Skills training is organized in two segments – review of homework practice from the preceding week and teaching of skills. The DBT skills group is not a processing group – meaning it is not a group where clients discuss and process individual challenges. It is a group that is led by a therapist and co-therapist, and is structured to teach clients behavioral skills to:
- Enhance a client’s abilities to interact with their environment
- Improve and maintain a client’s motivation to change and be engaged with treatment
- Ensure generalization of change occurring through treatment
- Enhance the motivation of therapists to deliver effective treatment
- Assist the individual in restructuring or changing their environment such that it supports and maintains progress and advancement towards goals
Between-Session Phone Coaching
Between-Session Phone Coaching is an opportunity to combine therapist feedback with instruction. The contact with the therapist is brief, focused, and target oriented. These coaching sessions are not a time for complaining and venting about personal problems, it is for help in using DBT skills. DBT therapists encourage clients to use skills coaching calls for:
- In-the-moment coaching using skills to effectively cope with situations that arise in everyday life
- Help in averting crisis behaviors prior to engaging in them (including self-injurious/suicidal behaviors)
- Reports of “good” news to therapist when a client has success in skills use
- Repairing any misunderstandings or behaviors that may interfere in the therapist/client relationship
The 5 areas of instability that clients may experience in daily life*
- Emotional Dysregulation
- Cognitive Instability
- Interpersonal Instability
- Behavior Instability
- Self Instability
*Cognitive-Behavioral Treatment of Borderline Personality Disorder, Marsha M. Linehan, 1993; p. 60
Information About Diagnoses:
- Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD)
https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/topics/borderline-personality-disorder/index.shtml - Dissociative Disorders and Dissociative Identity Disorder (DID)
https://www.nami.org/Learn-More/Mental-Health-Conditions/Dissociative-Disorders - Social Anxiety
https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/publications/social-anxiety-disorder-more-than-just-shyness/index.shtml - Generalized Anxiety
https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/publications/generalized-anxiety-disorder-gad/index.shtml
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/generalized-anxiety-disorder/symptoms-causes/syc-20360803 - Persistent Depressive Disorder
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/persistent-depressive-disorder/symptoms-causes/syc-20350929 - Major Depressive Disorder
https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/topics/depression/index.shtml - Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) and Acute Stress Disorder https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/topics/post-traumatic-stress-disorder-ptsd/index.shtml
We believe in the power of therapy.
We believe that acceptance and change can happen.
We believe that you can have a life worth living!

